A Guide to Traditional and Modern Distribution Rights for Film and TV Content (Part 4)
In this series, we’ve navigated the complex world of media distribution rights, revealing how these rights enable filmmakers and content creators to share their work with audiences globally. We began by exploring the foundational concepts of core and ancillary rights, emphasizing their critical role in the distribution landscape. We then ventured into the realm of physical distribution rights, discussing traditional methods such as theatrical releases, home video and non-theatrical screenings. Subsequently, we shifted our focus to non-physical distribution rights, breaking down the essential elements that drive content delivery and revenue in the digital era.
Now, in this final chapter, we shed light on the last category of non-physical distribution rights: Video-on-Demand (VOD). We will discuss various monetization models of VOD, providing insights into how these models shape viewer experiences and enhance content accessibility. Following this, we will revisit ancillary rights, presenting a comprehensive overview of the additional revenue streams that extend beyond core distribution channels.
Video-on-Demand (VOD) Distribution Rights
Video-on-Demand (VOD) distribution rights enable content creators to deliver their works directly to audiences via internet streaming platforms. Unlike traditional linear television broadcasting, which operates on a fixed schedule with viewers tuning in at predetermined times to watch content interspersed with commercials, VOD offers unparalleled flexibility and control. Viewers can select and watch content on demand, at any time, on various internet-connected devices. This non-linear approach allows for continuous viewing of multiple episodes, pausing and resuming content, and accessing a diverse range of programming tailored to individual preferences. This transition to on-demand consumption has revolutionized content accessibility and significantly transformed the Over-The-Top (OTT) entertainment landscape.
VOD distribution features a spectrum of monetization models, each suited to distinct audience preferences and content strategies. Let’s look into the four prominent VOD distribution rights models:
Free VOD (FVOD):
Free VOD platforms offer users access to content at no charge, removing financial barriers to content consumption. Viewers can watch videos without the need for subscription fees or transaction costs, ensuring easy accessibility for all. However, unlike other VOD models, FVOD services typically do not generate direct revenue from viewers. Instead, they rely on alternative sources such as donations, sponsorships or indirect means of support. Sometimes, creators or organizations use FVOD platforms to expand their audience reach and engagement, prioritizing accessibility over direct monetization.Advertising-Based VOD (AVOD):
Advertising-Based VOD platforms, similar to Free VOD, grant users access to content without any associated costs, ensuring widespread availability and ease of access. However, the primary distinction lies in the revenue model employed by AVOD platforms, which relies on advertisements. Users encounter ads either before, during or after viewing content, with the platform earning revenue from advertisers. This advertising revenue serves as the financial backbone, allowing AVOD platforms to offer free content to users while sustaining their operations.Subscription VOD (SVOD):
Subscription Video-on-Demand (SVOD) platforms operate on a subscription-based model, where users pay a regular fee for access to their content library. Subscribers enjoy an ad-free experience and unlimited streaming of movies, TV shows and even exclusive content at their convenience. SVOD platforms not only provide a reliable and recurring income stream but also offer subscribers a diverse and immersive entertainment experience spanning various genres and offerings.Transactional VOD (TVOD):
In contrast to Subscription VOD, Transactional VOD operates on a pay-per-transaction model, allowing users to rent or purchase individual titles for a one-time fee. With TVOD, viewers have on-demand access to the latest movie releases, premium content and other offerings without the long-term commitment associated with subscription-based services. This model is particularly popular for new movie releases, live events and exclusive content that may not be available on traditional streaming platforms. For content creators and distributors, TVOD offers a flexible distribution model that allows for targeted marketing and monetization strategies.
Ancillary distribution Rights
In the world of media distribution, content creators and rights holders have long recognized the value of ancillary distribution rights in maximizing revenue and expanding the reach of their intellectual property. Ancillary rights encompass a diverse array of opportunities beyond traditional distribution channels, offering new avenues for additional monetization and audience engagement. Understanding and strategically managing these rights is crucial for maximizing the potential of any creative project.
Here, we explore the details of four primary categories of ancillary distribution rights: Video Clips, Soundtrack, Format, Derivative Works and Merchandising, highlighting their significance and opportunities for content creators.
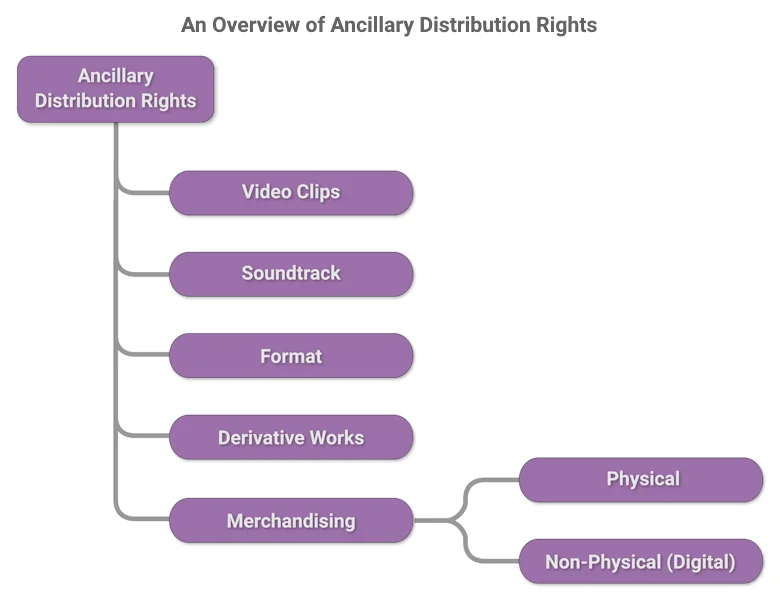
Video Clips
This involves licensing short excerpts or clips from the original content for various uses, such as promotional materials, advertisements, educational purposes, news segments and social media. Video clips can serve as teasers, highlight key moments or provide supplemental content that enhances the viewer’s engagement with the full work. Licensing video clips can be a lucrative source of income for the copyright holder, as they can be used across a wide range of platforms and media.
Soundtrack
These rights pertain to the music or audio components of the content, which can be licensed for use in other media productions, advertisements or sold as standalone products. Soundtracks can become valuable assets, contributing significantly to the overall brand identity of the content. They can be marketed through streaming platforms, physical album sales or incorporated into live performances and merchandise. Additionally, a well-received soundtrack can drive further engagement with the original content, enhancing its popularity and commercial success.
Format
Format rights encompass the intellectual property associated with a specific format or concept for media content, such as television shows, game shows or reality programs. This includes the fundamental structure, rules, themes and presentation style that define the essence of the program. Acquiring format rights grants production companies or broadcasters the permission to reproduce the same format in various markets or territories, tailoring it to suit local audiences while preserving the core elements of the original concept. This process enables the adaptation of content to different cultural contexts, languages and regulations, ensuring its relevance and appeal across diverse audiences worldwide.
Derivative Works
Derivative work rights are essentially the legal permission to create something new and creative that is inspired by or directly based on, the original work. This legal framework opens a door to a diverse landscape of derivative creations. These new works can take various forms, including adaptations that retell the story in different formats, such as novels based on movies or musicals based on TV shows. Additionally, they may involve prequels and sequels that expand upon the existing narrative by exploring backstories or continuing the storyline. Furthermore, derivative works can materialize as spin-off series, interactive video games or any other creative expression inspired by the original content.
Merchandising
Merchandising rights represent a crucial component of ancillary distribution in the media and entertainment industry, providing creators and rights holders with a strategic avenue to expand their intellectual property beyond its original form and into the realm of consumer products. These rights grant the legal authority to develop, produce and market merchandise inspired by the original content, spanning a diverse spectrum of physical and non-physical (digital) items:
- Physical:
Physical merchandising entails producing and selling tangible items that fans can buy and interact with. This includes products such as action figures, clothing, posters and accessories. These items enhance fan engagement and brand loyalty, turning fans into ambassadors who promote the content through their use of these goods, while also providing a significant revenue source for content creators and rights holders. - Non-Physical (Digital):
Non-physical merchandising, on the other hand, focuses on the creation of virtual or downloadable products that fans can access and enjoy through digital platforms. This encompasses a diverse range of digital goods and experiences, including mobile apps, desktop wallpapers, video games, e-books and virtual items within online communities and gaming environments. Digital merchandising leverages the power of technology and online distribution channels to reach audiences globally, offering immersive and interactive experiences that complement the original content.
Together, physical and digital merchandising rights afford content creators and rights holders the potential to create a multi-dimensional brand experience that surpasses traditional media boundaries. By strategically utilizing these rights, creators can deepen audience engagement, extend the lifespan of their intellectual property and unlock new revenue streams in an increasingly digital and connected world. From physical collectibles that fans proudly display on their shelves to engaging digital experiences that transport them into fantastical worlds, merchandising rights play a vital role in shaping the broader cultural impact and commercial success of entertainment franchises across the globe.
In conclusion, mastering media distribution rights is essential for creators to thrive in the dynamic entertainment landscape. Through a nuanced understanding and adept management of these rights, creators can forge impactful connections with global audiences, driving both cultural resonance and commercial success in an increasingly interconnected today’s world.
Visit our website or contact us today to learn more about how MediaRights can empower your business.

